Introduction
The pursuit of creating human-like robots has fascinated humanity for centuries. From early mechanical automatons to modern-day advanced robotics, the idea of machines that can mimic human behavior, appearance, and intelligence has captured our imagination. Today, with advancements in AI, robotics, and materials science, we are closer than ever to turning this dream into reality. But how close are we really? Can we expect fully autonomous, emotionally intelligent robots to walk among us in the near future? Let’s dive into the fascinating world of robotics and explore the progress, challenges, and implications of creating human-like robots.
The Evolution of Human-like Robots
Early Concepts and Early Automata
The idea of robots dates back to ancient civilizations. Myths and legends spoke of mechanical beings that could mimic human actions. However, it wasn’t until the 15th century that Leonardo da Vinci sketched plans for a humanoid robot, designed to mimic human motion. Yet, it wasn’t until the 20th century that robotics evolved from mere imagination into a serious scientific endeavor.
The Rise of Modern Robotics
The 1950s and 1960s marked the beginning of significant technological breakthroughs, with pioneers like George Devol and Joseph Engelberger laying the foundation for industrial robotics. These early robots were mechanical arms designed for factory work. Human-like robots—often referred to as “humanoids”—began to emerge, but their capabilities were limited, restricted mostly to rigid motions and basic tasks.
In the 1990s, the world saw its first humanoid robots, like Honda’s ASIMO, which could walk and interact with humans, albeit with jerky movements and limited responses.
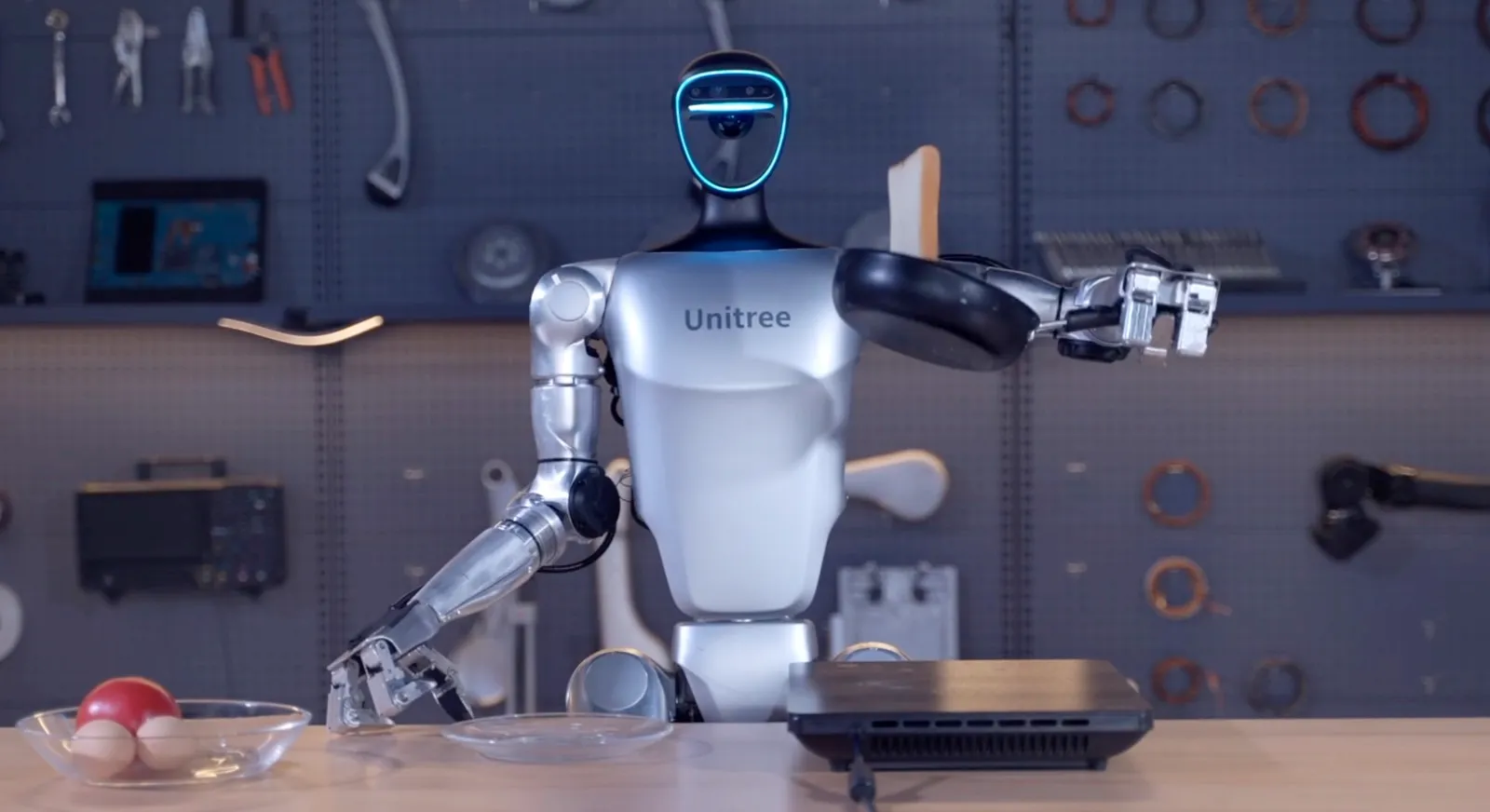

Advancements in Human-like Robotics
Artificial Intelligence: The Brain Behind the Robot
One of the most significant breakthroughs in human-like robotics is the integration of artificial intelligence (AI). AI algorithms allow robots to process information, learn from their environment, and make decisions based on data. This evolution marks a shift from simple pre-programmed machines to robots that can adapt, learn, and evolve over time. Companies like Boston Dynamics, Hanson Robotics, and Toyota are leading the charge, developing robots that not only mimic human movements but also exhibit complex behaviors.
Human-like Movements and Dexterity
In the early 21st century, robotics engineers began focusing on achieving more natural movements and dexterity. Robots like Boston Dynamics’ Atlas, capable of running, jumping, and performing backflips, showcase extraordinary advancements in balance and agility. Meanwhile, advancements in soft robotics have given rise to robots with more human-like flexibility, allowing them to perform delicate tasks such as handling fragile objects or assisting in medical procedures.
Facial Expressions and Emotional Intelligence
A critical aspect of making robots human-like is their ability to express emotions. This is not just about looking like a human, but about creating machines that can understand, process, and respond to human emotions. Robots like Hanson Robotics’ Sophia and Softbank’s Pepper are designed to read human emotions through facial expressions and voice tone. They can hold conversations and even exhibit facial expressions that mimic joy, sadness, or surprise. This emotional intelligence is crucial for applications in customer service, therapy, and education.
Challenges on the Path to Human-like Robots
Technical Challenges: Building the “Whole” Robot
While we’ve made impressive strides in various fields of robotics, creating a fully functional human-like robot remains an immense challenge. Some of the major hurdles include:
- Power Sources: Most robots rely on batteries, which limit their range and functionality. Until we develop more efficient and long-lasting power sources, robots will remain confined to short tasks or stationary roles.
- Mobility and Stability: The human body is extraordinarily complex. Achieving the dexterity of a human hand or the fluidity of human walking requires sophisticated design and materials that can mimic human anatomy. Even the most advanced humanoid robots today struggle with balance and coordination in dynamic environments.
- Sensor Integration: Robots need an extensive array of sensors to perceive their environment in real-time. This includes visual sensors (like cameras), tactile sensors (to feel), and auditory sensors (to hear). Integrating all these sensors to create a seamless interaction with the environment is a significant engineering challenge.
Ethical and Social Challenges
As robots become more advanced, ethical concerns begin to surface. These concerns are not just about the technology itself but also about how society will interact with these robots.
- Human-Robot Interaction: As robots become more human-like, the lines between humans and machines blur. This raises questions about how we should treat these robots—can we assign them rights? What happens when they start mimicking emotional connections?
- Job Displacement: With robots capable of performing tasks traditionally carried out by humans, there is an increasing concern about the displacement of workers in industries like manufacturing, healthcare, and retail.
- Security and Privacy: As robots gain more autonomy, they could become potential vectors for cyberattacks, raising concerns about data privacy, security breaches, and misuse of technology.
Applications of Human-like Robots
Healthcare and Assistance
One of the most promising areas for human-like robots is in healthcare. Robots like “Robear” in Japan and “Care-O-bot” in Europe are already being used in elder care facilities to assist with lifting and supporting elderly patients. Human-like robots can provide companionship and support, reducing the loneliness that many elderly individuals experience.
Moreover, robots can be designed to assist doctors in complex surgeries. With the help of AI, they can analyze patient data and even perform precision tasks, such as minimally invasive surgeries.
Customer Service and Hospitality
As robots become more adept at recognizing and understanding human emotions, their use in customer service will become more prevalent. Robots like Pepper are already deployed in retail stores to greet customers, provide information, and improve the customer experience.
In hospitality, humanoid robots can take over tasks like check-in, room service, or even acting as tour guides, offering personalized interactions with guests.
Entertainment and Companionship
The entertainment industry has also embraced humanoid robots. Robots like Sophia and the humanoid robots from the “Westworld” series showcase how robots can entertain, engage, and even form relationships with humans. These robots could become companions for people seeking social interaction in the future.
What Does the Future Hold?
The future of human-like robots is both exciting and uncertain. In the next few decades, we can expect several developments:
- Improved Human-Robot Integration: Future robots will likely be able to work alongside humans in complex environments like factories, hospitals, and homes, performing tasks with greater accuracy and efficiency.
- Enhanced AI Capabilities: As AI becomes more advanced, robots will be able to understand and predict human emotions more accurately, opening the door for deeper human-robot relationships.
- Ethical Regulation: Governments and tech companies will need to establish ethical guidelines and regulations to ensure robots are developed and used responsibly.
- Personal Robots: In the future, we may all have personal robots in our homes, capable of performing a variety of tasks, from cleaning to cooking to personal care.
Conclusion
While we are still far from achieving the fully autonomous, human-like robots depicted in science fiction, the progress we’ve made thus far is remarkable. As technology continues to evolve, the line between human and robot will become increasingly blurred. Yet, with these advancements come serious ethical, social, and technical challenges that we must navigate carefully. In the coming years, expect to see more robots in our everyday lives—whether as companions, helpers, or workers. The future is bright, but we must ensure we create these robots responsibly, with a clear understanding of the impact they will have on society.










































