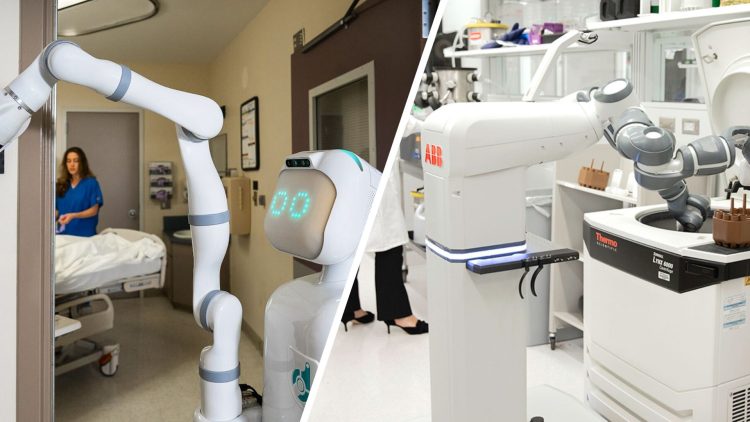
Introduction: The Rise of Robots in Daily Life
The 21st century is undeniably the era of robotics. From household assistants to industrial machines, robots are now an integral part of our everyday existence. But as these intelligent machines become more embedded into society, a pressing question arises: How safe are robots in daily life? This article explores the safety of robots, diving into their role in various sectors, the potential risks they pose, and the measures taken to ensure their safety.
The Role of Robots in Modern Society
Robots have evolved far beyond their initial use in factories. Today, they are present in various domains, including healthcare, transportation, entertainment, and even domestic chores. Below, we’ll explore how robots are integrated into these sectors and the safety considerations that come with their adoption.
1. Robots in Healthcare: A Life-Saving Revolution
Robotic technologies have made a remarkable impact in the medical field. Surgical robots, such as the da Vinci Surgical System, allow surgeons to perform minimally invasive operations with greater precision. Additionally, robots are used for rehabilitation, diagnostics, and even patient care through robotic nurses or companions.
Safety concerns: While these robots reduce human error and improve patient outcomes, their safety is paramount. Potential risks include malfunctioning equipment, incorrect data interpretation, or even cybersecurity threats if these devices are connected to hospital networks. Strict regulations and continuous monitoring of robotic systems ensure they meet the highest standards of reliability and accuracy.
Measures to ensure safety: The integration of safety protocols, such as redundant systems (backup systems in case of failure), regular maintenance checks, and real-time monitoring of robotic procedures, ensures the safety of patients and healthcare professionals. Furthermore, medical robots undergo rigorous testing and are subject to regulatory bodies like the FDA (Food and Drug Administration), ensuring they adhere to safety standards.
2. Robots in Transportation: Navigating Safety on the Road
Autonomous vehicles, or self-driving cars, represent one of the most ambitious applications of robotics in daily life. These robots are equipped with a combination of sensors, cameras, and AI systems to navigate roads without human intervention.
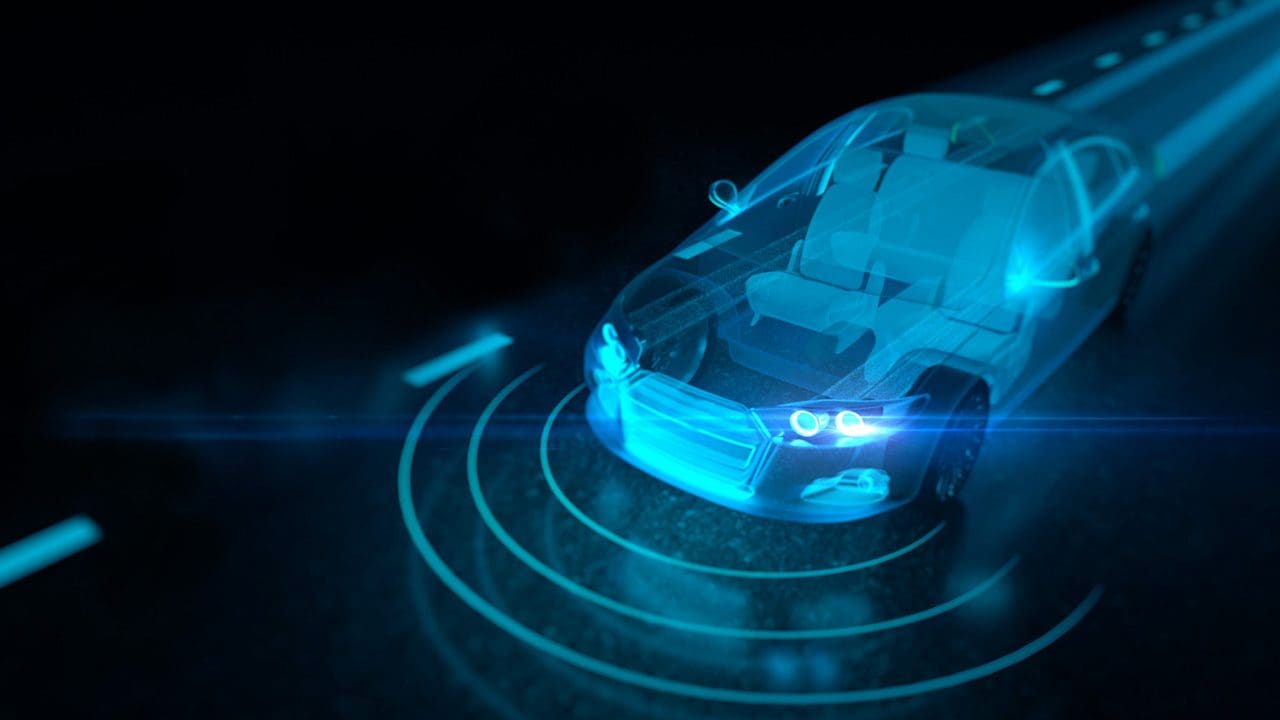

Safety concerns: The main safety issues surrounding autonomous vehicles are related to their ability to respond to unpredictable road conditions, such as weather changes, human drivers, and pedestrians. Accidents involving autonomous vehicles, while still rare, have raised concerns about the technology’s reliability.
Measures to ensure safety: Self-driving car manufacturers implement rigorous testing in both simulated environments and real-world scenarios to identify potential risks. The cars are designed with multiple redundancies, including backup sensors and fail-safe mechanisms, to ensure safe operation. Moreover, governments around the world are establishing laws and guidelines to regulate the development and deployment of autonomous vehicles, ensuring that they meet stringent safety standards before being allowed on the road.
3. Robots in the Home: A New Age of Domestic Assistance
Home robots, including robotic vacuum cleaners, lawn mowers, and even personal assistants like Amazon’s Alexa or Google Assistant, are becoming common household items. These robots are designed to perform routine tasks, freeing up time for their human users.
Safety concerns: While these robots can be a blessing in terms of convenience, there are certain safety risks, particularly with devices that involve movement or interaction with people. For example, robotic vacuums have occasionally caused damage to furniture or even posed tripping hazards. Moreover, privacy concerns arise when home assistants record personal data.
Measures to ensure safety: Manufacturers implement numerous safety features, such as collision detection, emergency stop buttons, and software that allows robots to avoid obstacles. As for privacy, encryption and opt-out features allow users to control what information their devices gather. Additionally, regulations around data privacy are becoming stricter, ensuring that robots respect the privacy of their owners.
4. Robots in Industry: Efficiency and Precision at Scale
Industrial robots have been transforming manufacturing and production lines for decades. From assembling cars to packaging products, these robots are designed to perform tasks with high precision and speed.
Safety concerns: Industrial robots are often large, powerful machines capable of performing dangerous tasks. While they improve productivity and reduce human labor in hazardous environments, they also pose risks such as injuries from mechanical failures or unsafe interactions with human workers.
Measures to ensure safety: Advanced safety systems are integrated into industrial robots, such as sensors that detect human presence and automatically halt operations to prevent accidents. Additionally, safety standards, such as ISO 10218, guide the design and operation of industrial robots, ensuring that they operate within safe parameters.
Potential Risks of Robots in Daily Life
While robots undoubtedly offer numerous benefits, they also bring with them certain risks. Some of these risks are inherent in the technology itself, while others stem from the human interaction with robots.
1. Cybersecurity Threats
As robots become more connected to the internet and other networks, they become potential targets for cyberattacks. Hackers could gain control over autonomous vehicles, medical robots, or even home assistants, leading to severe consequences.
Example: In 2017, the ransomware attack “WannaCry” affected medical devices in several hospitals, highlighting the vulnerability of networked systems. Such breaches raise questions about the security of robots that rely on connectivity.
Measures to mitigate risk: To combat these threats, manufacturers are incorporating robust encryption protocols, regular software updates, and firewall protections. Additionally, researchers are developing more secure systems, like blockchain, to prevent unauthorized access to robots and their data.
2. Ethical and Legal Concerns
The widespread use of robots raises a host of ethical and legal questions. For instance, if an autonomous vehicle causes an accident, who is held accountable? What if a medical robot misdiagnoses a patient or fails during surgery? These issues could complicate liability and accountability in the case of robot malfunctions.
Measures to address concerns: Governments are increasingly enacting laws to govern the use of robots, establishing frameworks for liability, accountability, and safety. Additionally, ethical guidelines are being formulated by organizations such as the IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers) to ensure that robots are designed and used in a way that prioritizes human safety and well-being.

3. Social Impact: Job Displacement
The rise of robots in daily life has led to concerns about job displacement. As robots take over more tasks, from manufacturing to customer service, many fear that human workers will be replaced by machines, leading to unemployment and economic instability.
Measures to address concerns: While automation can displace certain types of jobs, it can also create new opportunities. Governments and organizations are focusing on reskilling initiatives to help workers transition into new roles that require human creativity, decision-making, and emotional intelligence—qualities that robots cannot replicate. Additionally, the development of collaborative robots (cobots), which work alongside humans, helps mitigate the impact of automation by assisting rather than replacing workers.
Ensuring the Safety of Robots: A Collaborative Effort
The safety of robots in daily life is a multifaceted challenge that requires collaboration among various stakeholders, including manufacturers, governments, and users. Ensuring that robots are safe and reliable involves continuous innovation and oversight.
1. Manufacturers’ Role in Ensuring Safety
Robotic manufacturers are at the forefront of ensuring safety by designing robots that meet international safety standards. This involves rigorous testing, developing safety features like emergency stop buttons and obstacle detection, and complying with industry regulations.
2. Government Regulations and Oversight
Governments play a key role in regulating the use of robots, establishing legal frameworks that govern their deployment and ensuring that they meet safety standards. For instance, the European Union has proposed AI regulations to ensure the ethical use of robots, while the U.S. National Highway Traffic Safety Administration has guidelines for autonomous vehicles.
3. User Education and Awareness
Users also have a responsibility in ensuring the safe operation of robots. Proper maintenance, software updates, and understanding the robot’s capabilities and limitations are essential to avoiding accidents and maximizing the benefits of robotic technologies.
Conclusion: The Future of Robotic Safety
As robots continue to evolve and become more integrated into our daily lives, the question of safety will remain at the forefront of technological development. With the right precautions, the risks associated with robots can be mitigated, and their benefits can be fully realized. By working together—manufacturers, governments, and users—we can ensure that robots continue to enhance our lives without compromising our safety.