In recent decades, the global economic landscape has been witnessing a shift in power. Emerging economies, particularly in regions like Asia, Africa, and Latin America, are increasingly becoming significant players on the world stage. With their rapid growth, vast populations, and expanding middle classes, these economies are poised to reshape industries globally. The influence of these emerging markets is not just limited to trade and investment flows but extends to the fundamental structures of global industries.
In this article, we explore how emerging economies are transforming various sectors, including manufacturing, technology, energy, and consumer markets. We also examine the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead for companies operating within these markets.
The Rise of Emerging Economies
Emerging economies, often referred to as developing or frontier markets, represent nations in transition, characterized by fast-paced industrial growth, increased foreign investment, and improving standards of living. Countries such as China, India, Brazil, and South Africa have already had significant impacts, while nations like Vietnam, Nigeria, and Mexico are rapidly gaining importance.
The rise of these economies is not a new phenomenon. However, their role in global markets is becoming more pronounced due to several key factors:
- Demographic Shifts: Emerging economies are home to a large portion of the world’s population, particularly the youth. According to the United Nations, nearly 85% of the world’s population growth between now and 2050 will come from developing countries.
- Urbanization: Urban centers in emerging economies are growing rapidly, creating new demand for infrastructure, technology, and consumer goods. This is changing how industries design, produce, and distribute their products and services.
- Technological Leapfrogging: In many cases, emerging markets are skipping over traditional technological development phases, such as landline phones or wired internet, in favor of mobile technology and digital solutions.
- Globalization of Trade: The integration of emerging economies into the global supply chain has accelerated trade and investment flows, opening up new opportunities for industries across the world.
These factors are not only expanding the market size in these economies but are also challenging established industry leaders to innovate and adapt.
Manufacturing and Supply Chain Transformation
Emerging economies are transforming the global manufacturing landscape, with China leading the charge as the world’s factory. But as labor costs in China rise, companies are increasingly turning to other emerging markets, including India, Vietnam, and Mexico, for more cost-effective manufacturing options.
1. Shifting Global Supply Chains
As labor costs in traditionally low-cost manufacturing hubs increase, companies are diversifying their supply chains to other emerging markets. This has led to a shift in the global distribution of manufacturing. Southeast Asia, for example, has become an attractive destination for companies seeking lower labor costs and more competitive business environments.
India is emerging as a key player in manufacturing, especially in sectors like electronics, textiles, and automotive. The government’s “Make in India” initiative has further accelerated this shift by encouraging foreign direct investment (FDI) and providing tax incentives for manufacturers to set up operations.
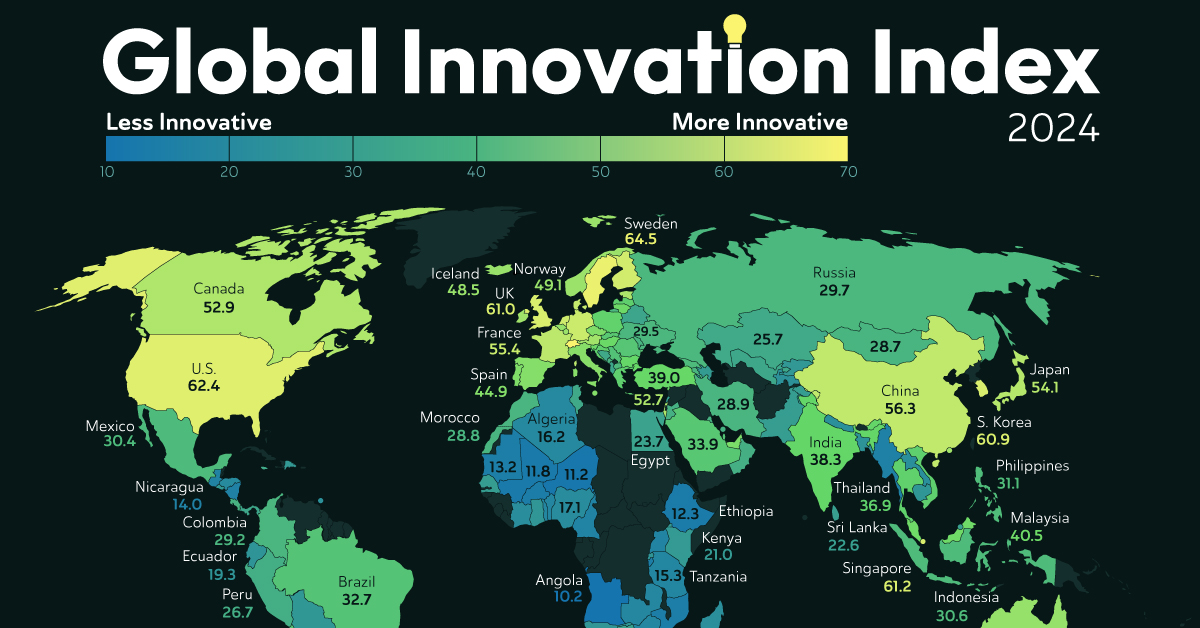
2. Automation and Smart Manufacturing
While low labor costs have historically been a major advantage for emerging economies, automation is now playing a significant role in transforming manufacturing processes. The increasing adoption of Industry 4.0 technologies—such as artificial intelligence (AI), robotics, and the Internet of Things (IoT)—is reshaping production processes worldwide.
For example, factories in India and China are implementing robotics and AI-driven supply chain management to reduce inefficiencies, improve quality, and increase productivity. This move toward automation is making these economies even more competitive, as they combine low-cost labor with cutting-edge technology.
Technology and Digital Transformation
The technological revolution is one of the most profound ways emerging economies are influencing global industries. While developed nations have historically been at the forefront of technological innovation, emerging markets are now setting the pace in some key sectors.
1. Fintech and Digital Payments
Emerging economies are leapfrogging traditional banking systems and embracing digital payments, particularly in regions like Africa and Asia. Countries such as Kenya, with mobile payment systems like M-Pesa, are leading the way in financial inclusion. These innovations are opening up new opportunities for businesses and consumers alike, enabling cross-border transactions, reducing transaction costs, and increasing access to capital.
In India, the government’s push for a cashless society, through platforms like UPI (Unified Payments Interface), is revolutionizing how people conduct transactions. This digital transformation is not only changing consumer behavior but is also creating new markets for fintech companies and enabling the rise of digital currencies.
2. E-commerce and Online Retail
The rapid growth of internet penetration in emerging economies has fueled the rise of e-commerce and online retail. Companies such as Alibaba in China and Flipkart in India have become regional giants, offering everything from consumer electronics to groceries.
In Africa, e-commerce platforms like Jumia are capitalizing on the growing internet connectivity, changing how consumers shop and access goods and services. With the rise of online shopping, businesses must rethink their distribution strategies, ensuring products are delivered efficiently across diverse and often remote locations.
3. Tech Talent and Innovation Hubs
The growing pool of skilled labor in emerging economies is transforming global tech industries. India, in particular, has long been a hub for IT outsourcing, but it is now also seeing an increase in homegrown tech startups. The rise of Silicon Valley-like hubs in cities like Bengaluru and Nairobi reflects the growing entrepreneurial spirit and technological innovation in these regions.
These innovation hubs are helping emerging economies move beyond simple adoption of technology to becoming leaders in tech development. The demand for software engineers, data scientists, and AI specialists is growing exponentially, attracting global investments and fostering innovation.
Energy and Sustainability
As the world faces pressing environmental challenges, emerging economies are poised to play a pivotal role in the future of global energy markets. While historically these nations have been major consumers of fossil fuels, there is a growing trend toward renewable energy adoption.
1. Renewable Energy Investments
Many emerging economies, especially in Asia and Africa, are embracing renewable energy sources to meet their growing energy needs while addressing climate change. China, for instance, is the world leader in solar energy production, while India is rapidly expanding its wind and solar capacity as part of its ambitious climate goals.
In Africa, countries like Kenya and South Africa are leading the charge in geothermal and wind energy projects. This shift is not only essential for sustainability but also opens up new industries and markets for clean energy technologies and green jobs.

2. Sustainable Practices in Agriculture and Manufacturing
Emerging economies are increasingly recognizing the need for sustainable practices in agriculture and manufacturing. Innovations such as precision farming, sustainable water management, and waste-to-energy technologies are being adopted to reduce the environmental impact of these industries.
For example, Brazil, a major agricultural producer, is investing in sustainable farming practices to reduce deforestation in the Amazon while increasing productivity. Similarly, industries in China and India are adopting cleaner production techniques to meet stricter environmental regulations and improve their global competitiveness.
Consumer Markets and Changing Demographics
The growing middle class in emerging economies is one of the most significant drivers of change in global consumer markets. As more people move out of poverty and gain access to disposable income, their consumption patterns are beginning to mirror those of developed nations.
1. Rising Disposable Incomes and Changing Consumption
The rapid rise in disposable incomes in countries like China, India, and Brazil is reshaping global consumer demand. In particular, these consumers are increasingly interested in higher-quality products, luxury goods, and Western brands. This trend is forcing multinational companies to rethink their product offerings, marketing strategies, and supply chains to cater to the tastes and preferences of consumers in emerging markets.
2. The Digital Consumer
With increased internet connectivity, emerging economies are seeing a surge in digital consumption. From social media and online shopping to digital entertainment and streaming services, the digital economy is transforming the way consumers interact with brands and products.
China’s thriving e-commerce platforms, such as Taobao and Tmall, along with India’s burgeoning mobile internet user base, are examples of how digital technology is reshaping consumer behavior. Companies that can leverage these digital platforms will gain a competitive edge in these rapidly growing markets.
Challenges and Opportunities
While emerging economies present significant opportunities for global industries, they also come with their fair share of challenges. Companies seeking to tap into these markets must navigate complex regulatory environments, political instability, and cultural differences.
However, those that can successfully adapt to local conditions, understand consumer preferences, and invest in innovation will be well-positioned to succeed in these dynamic markets. Additionally, as these economies continue to grow, they will become important sources of innovation, driving global trends in technology, sustainability, and manufacturing.
Conclusion
Emerging economies are not just passive players in the global economic landscape; they are actively reshaping industries across the globe. As these markets continue to grow, they will drive innovation, disrupt traditional business models, and create new opportunities for global businesses.
For industries looking to succeed in the future, understanding the dynamics of these emerging economies and investing in sustainable, innovative solutions will be key to navigating the shifting economic tides.










































