In the midst of rapid technological advancements and the global shift toward digital economies, one question lingers: Can digitalization help revive traditional industries that are struggling to keep up with modern demands? This article delves into how digital transformation could breathe new life into sectors that have long relied on conventional practices, examining both the challenges and opportunities of integrating digital technologies into age-old industries.
The Growing Importance of Digitalization
The term digitalization is often used to describe the integration of digital technologies into all aspects of human life, from personal communication to business processes. For industries that have traditionally operated in slower, more methodical ways, digitalization offers a path forward to remain competitive, efficient, and relevant in today’s fast-paced economy.
For example, industries like manufacturing, agriculture, construction, and even the arts have all seen significant transformations in the way they operate, thanks to the advent of digital technologies. By implementing digital tools—ranging from Internet of Things (IoT) devices to Artificial Intelligence (AI)—traditional industries can enhance their productivity, improve customer engagement, and reduce operational costs.
Traditional Industries: A Brief Overview
Before we dive into how digitalization can specifically benefit these industries, it’s important to first understand the challenges these sectors face.
- Manufacturing: Often characterized by large-scale operations, complex supply chains, and significant labor costs, the manufacturing industry has long relied on traditional methods for production, inspection, and logistics.
- Agriculture: The backbone of many economies, agriculture has been slow to modernize, with many farms still using conventional equipment and techniques. Issues like labor shortages, climate change, and supply chain inefficiencies continue to plague the sector.
- Retail: While not as “traditional” as manufacturing or agriculture, brick-and-mortar retail still faces stiff competition from e-commerce giants, struggling with customer engagement and experience in the digital age.
- Construction: Construction industries have a reputation for being slow to adopt new technologies. Many construction projects are marred by budget overruns, delays, and inefficiencies—problems exacerbated by outdated workflows.
Digital Tools Transforming Traditional Industries
Digital technologies offer a range of innovative solutions that can modernize these industries, resulting in greater productivity, efficiency, and sustainability.
1. The Internet of Things (IoT)
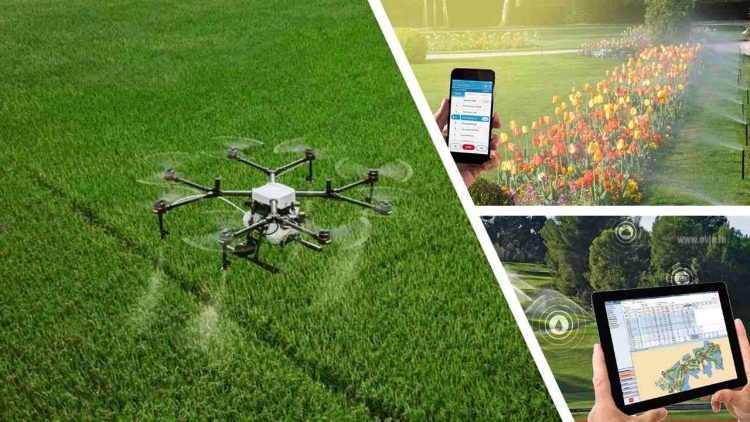
In manufacturing, IoT can create “smart factories,” where machines communicate with each other to optimize production and minimize downtime. Sensors embedded in machinery can detect malfunctions before they happen, providing real-time data that can be used to predict failures, saving time and money. Additionally, IoT applications in agriculture—such as smart irrigation systems and precision farming—can optimize water usage and monitor soil health.
Example: In agriculture, drones equipped with sensors can monitor crop health, soil moisture, and pest presence, enabling farmers to make data-driven decisions for improved yields and cost savings.
2. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning
AI is another game-changer. By harnessing vast amounts of data, AI can be used to automate processes, optimize supply chains, and improve customer service. In manufacturing, predictive analytics powered by AI can streamline production scheduling and reduce waste. In retail, machine learning algorithms can personalize shopping experiences, offering tailored product recommendations.
Example: In construction, AI-driven software can analyze blueprints and designs, suggesting modifications that can reduce costs or improve safety—transforming the way architects and engineers collaborate.
3. Cloud Computing
Cloud computing offers a central platform where information can be stored and accessed in real time. This allows traditional industries to streamline communication, increase collaboration, and reduce IT infrastructure costs. The construction sector, for instance, can benefit from cloud-based project management tools that enable teams to coordinate more efficiently, even if they are spread across different locations.
Example: In retail, cloud-based point-of-sale systems allow businesses to track inventory in real time, improving stock management and ensuring they meet consumer demand without overstocking.
4. Blockchain Technology
Though still emerging, blockchain has the potential to revolutionize industries like agriculture and manufacturing by ensuring the transparency, traceability, and security of transactions. For example, blockchain can be used to track the origins of food products, providing consumers with transparency regarding sustainability and ethical sourcing.
Example: In the fashion industry, blockchain can track the journey of textiles from source to store, offering consumers a deeper understanding of where their clothing comes from and how it was made.
Key Benefits of Digitalization for Traditional Industries
1. Increased Efficiency and Automation
One of the primary benefits of digitalization is the ability to automate routine tasks, freeing up human workers to focus on more strategic or creative tasks. For instance, in manufacturing, robots can be used for repetitive assembly tasks, while in agriculture, automation in planting and harvesting can save farmers significant labor costs.
2. Enhanced Decision Making
The use of big data analytics empowers businesses to make better decisions, backed by evidence and real-time data. Manufacturing companies can analyze production data to identify bottlenecks and inefficiencies, while farmers can use weather data and soil analytics to optimize planting schedules.
3. Improved Customer Engagement
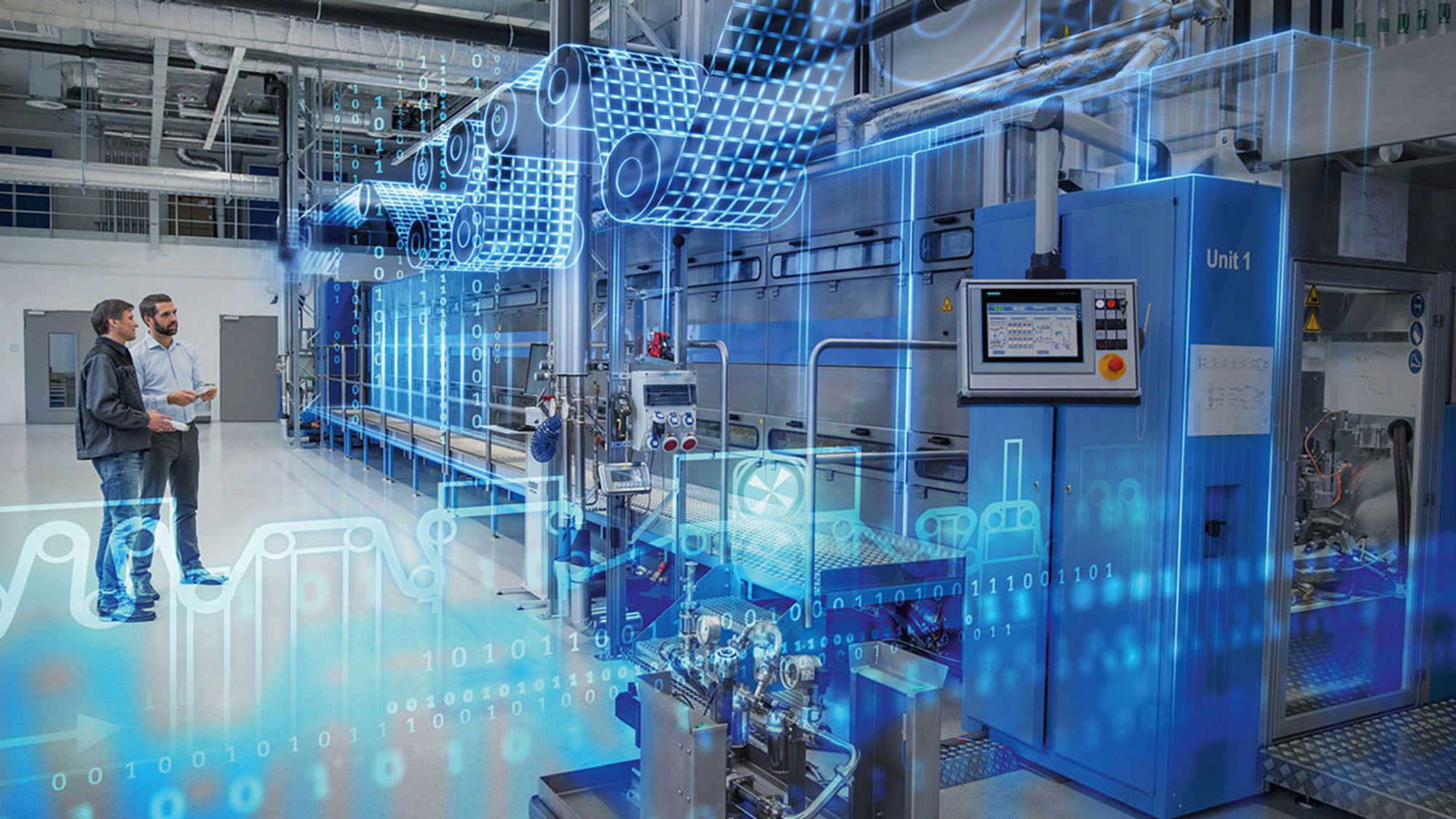

Digital tools allow businesses to engage with customers more effectively. In retail, for example, online platforms enable personalized shopping experiences, while manufacturing companies can use customer feedback to refine products or services. Social media platforms also offer a unique opportunity to engage directly with consumers, gathering insights to drive future innovation.
4. Environmental Sustainability
With the pressure to reduce carbon footprints and adopt more sustainable practices, digitalization can play a significant role. Smart grids in energy management, for example, can reduce energy waste in manufacturing. In agriculture, precision farming allows for more sustainable land use by optimizing water and fertilizer usage.
Challenges to Digitalization in Traditional Industries
Despite the clear advantages, the path to digitalization is not without obstacles. Some of the key challenges include:
1. High Initial Costs
The upfront investment required to implement digital technologies—whether it’s for new software, machinery, or training—can be a significant barrier for companies with tight margins or those operating on a small scale.
2. Resistance to Change
Many workers in traditional industries are used to conventional processes and may resist adopting new technologies. Training employees to use new systems or machines can also be time-consuming and costly.
3. Cybersecurity Risks
As more devices are connected to the internet, the risk of cyber-attacks increases. Industries that handle sensitive data—such as healthcare, manufacturing, or agriculture—must invest heavily in robust cybersecurity measures to protect their systems.
4. Data Integration Issues
Integrating new digital tools into existing systems can be a complex and time-consuming process. Ensuring that all systems, from inventory management to customer service, work seamlessly together is essential for smooth operations.
The Future of Digitalization in Traditional Industries
Looking ahead, the potential for digitalization in traditional industries is immense. As technologies continue to evolve, we will likely see even more powerful tools that can further enhance productivity and innovation. Technologies like 5G, augmented reality (AR), and virtual reality (VR) will further transform sectors like retail, manufacturing, and construction.
For instance, augmented reality could allow customers to “try on” clothes or visualize furniture in their homes before making a purchase, while 5G will enable faster, more reliable communication between machines in factories, driving automation to new levels.
In conclusion, digitalization offers an invaluable opportunity for traditional industries to revitalize and future-proof themselves against the evolving business landscape. While there are certainly challenges to overcome, the long-term benefits—ranging from increased efficiency to improved customer experiences—make digital transformation a key driver of success. The journey may be complex, but it’s a path worth exploring for industries looking to remain competitive in the digital age.










































